Difference between revisions of "RidgeRun OpenCV Fork"
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
=== GStreamer Video Capture === | === GStreamer Video Capture === | ||
| + | |||
| + | **STATUS**: Submitted. | ||
Effectively removes the memory copy when transferring data from the GstBuffer to the cv::Mat. Now the GstBuffer and its associated memory will remain alive throughout the lifespan of the matrix. | Effectively removes the memory copy when transferring data from the GstBuffer to the cv::Mat. Now the GstBuffer and its associated memory will remain alive throughout the lifespan of the matrix. | ||
| Line 48: | Line 50: | ||
g++ -o benchmark benchmark.cc $(pkg-config --cflags --libs opencv4$) -std=c++11 | g++ -o benchmark benchmark.cc $(pkg-config --cflags --libs opencv4$) -std=c++11 | ||
GST_DEBUG=perf:4 ./benchmark | GST_DEBUG=perf:4 ./benchmark | ||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | |||
| + | === GStreamer Main Loop === | ||
| + | |||
| + | Optionally enables a GMainLoop when capturing using GStreamer Video Capture. | ||
| + | |||
| + | A running GMainLoop processes many events on the GLib/GStreamer world. While some things may work without it, many others won't. Examples of these are signals, timers and many other source events. The problem becomes more concerning by the fact that some GStreamer elements rely on signals to work. This branch allows the user to specify an OpenCV option to start a main loop, if needed. Since the loop blocks, this is done in a separate thread. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Use the following environment variable to enable the main loop: | ||
| + | OPENCV_VIDEOIO_GSTREAMER_START_MAINLOOP=true | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Tested under the following conditions | ||
| + | * OpenCV Version: 4.4.0 | ||
| + | * Mainloop used by [https://github.com/ridgerun/gst-shark GstShark] tracers. | ||
| + | * Jetson Nano | ||
| + | * The following source: | ||
| + | <source lang=c++> | ||
| + | #include <opencv2/opencv.hpp> | ||
| + | |||
| + | int main() { | ||
| + | cv::VideoCapture cap("videotestsrc is-live=true ! fakesink", cv::CAP_GSTREAMER); | ||
| + | |||
| + | while(1){ | ||
| + | cv::Mat frame; | ||
| + | cap >> frame; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | cap.release(); | ||
| + | return 0; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | * Run with | ||
| + | <source lang=bash> | ||
| + | g++ -o mainloop mainloop.cc $(pkg-config --cflags --libs opencv4$) -std=c++11 | ||
| + | OPENCV_VIDEOIO_GSTREAMER_START_MAINLOOP=false GST_DEBUG=GST_TRACER:7 GST_TRACERS=framerate ./mainloop | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
[[File:RR_opencv_fork_max_framerate.png|thumb|center|500px|GStreamer Video Capture - Max Framerate]] | [[File:RR_opencv_fork_max_framerate.png|thumb|center|500px|GStreamer Video Capture - Max Framerate]] | ||
Revision as of 21:25, 1 October 2020
Introduction
The RidgeRun OpenCV fork is a modified version of the project with various improvements around speed and efficiency. While some changes are general (i.e.: any platform will benefit from them), others are specific to the NVIDIA Jetson family.
The fork is hosted at:
https://github.com/RidgeRun/opencv
Contents
Building the Project
Follow the instructions in our Compiling OpenCV from Source page. Make sure you select:
- RidgeRun fork
- GStreamer support
- CUDA support (if applicable)
Enhancements
GStreamer Video Capture
**STATUS**: Submitted.
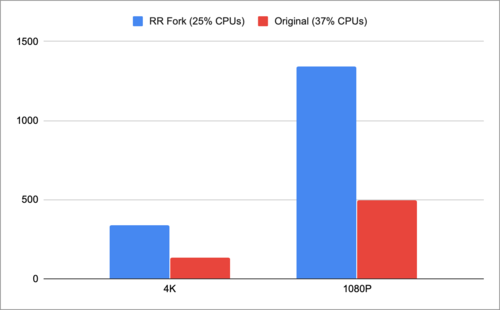
Effectively removes the memory copy when transferring data from the GstBuffer to the cv::Mat. Now the GstBuffer and its associated memory will remain alive throughout the lifespan of the matrix.
Tested under the following conditions
- OpenCV Version: 4.4.0
- FPS and CPU usage taken with the GstPerf element.
- Jetson Nano
- The following source:
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
int main() {
cv::VideoCapture cap(
"fakesrc sizetype=fixed filltype=zero sizemax=24883200 ! video/x-raw,format=BGR,width=3840,height=2160 ! "
"perf print-arm-load=true ! appsink drop=false sync=false max-buffers=3",
cv::CAP_GSTREAMER);
while(1){
cv::Mat frame;
cap >> frame;
}
cap.release();
return 0;
}
- Run with
g++ -o benchmark benchmark.cc $(pkg-config --cflags --libs opencv4$) -std=c++11
GST_DEBUG=perf:4 ./benchmark
GStreamer Main Loop
Optionally enables a GMainLoop when capturing using GStreamer Video Capture.
A running GMainLoop processes many events on the GLib/GStreamer world. While some things may work without it, many others won't. Examples of these are signals, timers and many other source events. The problem becomes more concerning by the fact that some GStreamer elements rely on signals to work. This branch allows the user to specify an OpenCV option to start a main loop, if needed. Since the loop blocks, this is done in a separate thread.
Use the following environment variable to enable the main loop:
OPENCV_VIDEOIO_GSTREAMER_START_MAINLOOP=true
Tested under the following conditions
- OpenCV Version: 4.4.0
- Mainloop used by GstShark tracers.
- Jetson Nano
- The following source:
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
int main() {
cv::VideoCapture cap("videotestsrc is-live=true ! fakesink", cv::CAP_GSTREAMER);
while(1){
cv::Mat frame;
cap >> frame;
}
cap.release();
return 0;
}
- Run with
g++ -o mainloop mainloop.cc $(pkg-config --cflags --libs opencv4$) -std=c++11
OPENCV_VIDEOIO_GSTREAMER_START_MAINLOOP=false GST_DEBUG=GST_TRACER:7 GST_TRACERS=framerate ./mainloop