Difference between revisions of "Template:BIPS/Main contents"
(→Supported Formats) |
(→What is Buffer Interprocess Sharing?) |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
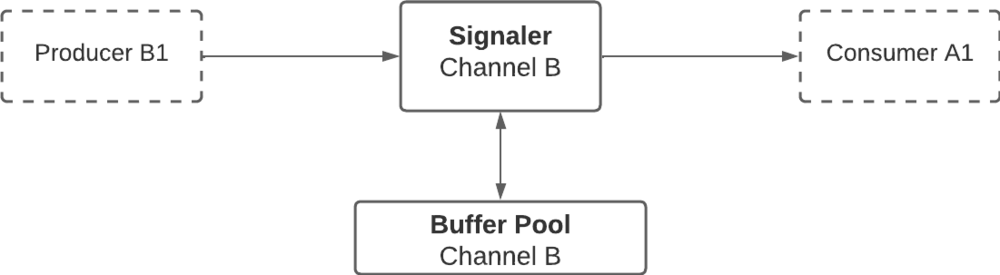
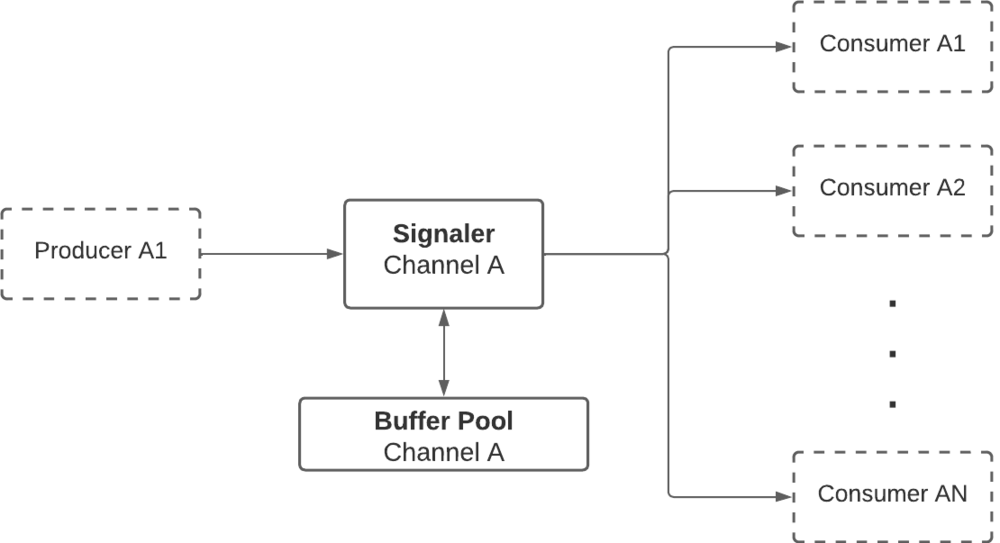
Buffer Interprocess Sharing or BIPS is a variant of a common IPC that allows communication between processes. In this case, BIPS allows sharing of data buffers between two or more processes. Classified as Producers or Consumers, according to their role in the system. The producer is in charge of generating and filling the information of the buffers, that Consumers will read. The synchronization between these entities is handled by the Signaler, which ensures that all operations are concurrent-safe. This means that Consumers can only read buffers that are fully written by Producers, and that Producers can only write buffers that are no longer being read by Producers. These buffers are created and managed by a shared structure known as the Buffer Pool which has a fixed capacity. Again, the synchronization between the BP and the Consumers/Producers is handled by the Signaler. | Buffer Interprocess Sharing or BIPS is a variant of a common IPC that allows communication between processes. In this case, BIPS allows sharing of data buffers between two or more processes. Classified as Producers or Consumers, according to their role in the system. The producer is in charge of generating and filling the information of the buffers, that Consumers will read. The synchronization between these entities is handled by the Signaler, which ensures that all operations are concurrent-safe. This means that Consumers can only read buffers that are fully written by Producers, and that Producers can only write buffers that are no longer being read by Producers. These buffers are created and managed by a shared structure known as the Buffer Pool which has a fixed capacity. Again, the synchronization between the BP and the Consumers/Producers is handled by the Signaler. | ||
| − | [[File:bips_flow2.png|1000px| | + | [[File:bips_flow2.png|1000px|frameless|center|BIPS communication between two processes]] |
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| − | [[File:bips_flow1.png|1000px| | + | [[File:bips_flow1.png|1000px|frameless|center|BIPS communication betwen one Producer and N Consumers]] |
Revision as of 00:44, 6 December 2022
|
Buffer Interprocess Sharing! Buffer Interprocess Sharing. |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Buffer Interprocess Sharing | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
This wiki is a user guide for our Buffer Interprocess Sharing project. What is Buffer Interprocess Sharing?Buffer Interprocess Sharing or BIPS is a variant of a common IPC that allows communication between processes. In this case, BIPS allows sharing of data buffers between two or more processes. Classified as Producers or Consumers, according to their role in the system. The producer is in charge of generating and filling the information of the buffers, that Consumers will read. The synchronization between these entities is handled by the Signaler, which ensures that all operations are concurrent-safe. This means that Consumers can only read buffers that are fully written by Producers, and that Producers can only write buffers that are no longer being read by Producers. These buffers are created and managed by a shared structure known as the Buffer Pool which has a fixed capacity. Again, the synchronization between the BP and the Consumers/Producers is handled by the Signaler.
Supported FormatsBIPS is used to communicate processes that need to share information, which helps to optimize memory usage and applications performances. The Shared Memory method uses a common memory space to read and write data, where synchronization is performed by means of some scheduling method (semaphores) to employ the use of the shared resource. On the other hand, the Message Passing method, specifically speaking of the use of the NvSci API, provides a communication channel where two totally independent processes can share data with each other without worry about memory faults.
Shared Memory common example
Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
Message Passing common example
Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
Tested Platforms
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
RidgeRun Support | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
RidgeRun provides support for embedded Linux development for NVIDIA, Xilinx, Freescale/NXP, and Texas Instruments platforms, specializing in multimedia applications. This page contains detailed guides and information on how to get started with Buffer Interprocess Sharing and start using its full capabilities. To get up-to-speed with your Buffer Interprocess Sharing, start by clicking below:
Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||