Difference between revisions of "Template:BIPS/Main contents"
(→What is Buffer Interprocess Sharing?) |
|||
| (18 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| + | <table> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td> | ||
| + | {{NVIDIA Preferred Partner logo}} | ||
| + | <td> | ||
| + | <center> | ||
| + | {{ContactUs Button}} | ||
| + | </center> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | </table> | ||
| valign="center" style="text-align:center;" | | | valign="center" style="text-align:center;" | | ||
| rowspan="5" valign="top" style="text-align:center;" | {{BIPS/TOC}} | | rowspan="5" valign="top" style="text-align:center;" | {{BIPS/TOC}} | ||
| Line 13: | Line 23: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | width="100%" valign="top" colspan=" | + | | width="100%" valign="top" colspan="3" style="background-color: #4d6d9a; font-weight: bold; text-align: center; color:#ffffff"| |
Buffer Interprocess Sharing | Buffer Interprocess Sharing | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | width="100%" valign="top" colspan=" | + | | width="100%" valign="top" colspan="3"| |
| − | This wiki is a user guide for our '''Buffer Interprocess Sharing''' project. | + | This wiki is a user guide for our '''Buffer Interprocess Sharing''' project. |
==What is Buffer Interprocess Sharing?== | ==What is Buffer Interprocess Sharing?== | ||
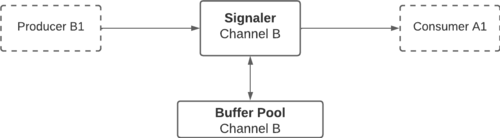
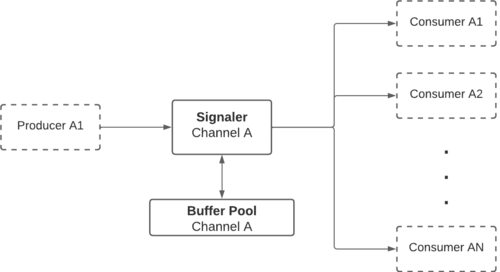
| − | + | Buffer Interprocess Sharing, or BIPS, is '''RidgeRun's optimized IPC library''' fully compatible with '''C++''' and '''Python'''. In this case, BIPS allows sharing of data buffers between two or more processes with zero copy. They can be classified as Producers or Consumers according to their role in the system. The producer is responsible for generating and filling in the information on the buffers that the Consumers will read. The synchronization between these entities is handled by the Signaler, which ensures that all operations are concurrent-safe. This means that Consumers can only read buffers that are fully written by Producers and that Producers can only write buffers already read by Producers. These buffers are created and managed by a shared structure known as the Buffer Pool, which has a fixed capacity. The Signaler handles the synchronization between the BP and the Consumers/Producers. | |
| − | Buffer Interprocess Sharing or BIPS is | + | |- |
| + | | width="100%" valign="top" colspan="3"| | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
| Line 34: | Line 45: | ||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
| − | + | ==Use cases== | |
| + | |||
| + | ''Wondering how and when to use BIPS?'' | ||
| + | BIPS is a solution to exchange memory buffers between two isolated processes with zero copies without requiring additional processes. You can find BIPS in the following use cases: | ||
| − | + | * '''Buffer exchange between C++ and Python''' | |
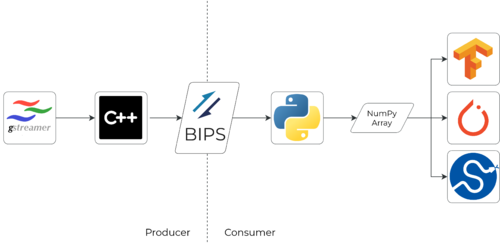
| − | + | BIPS allows communication between '''C++ and Python''' back and forth. A particular case is using a GStreamer capture application that requires transmitting the frames captured by a camera to a PyTorch-based Python application. From C++, you can define an agnostic memory buffer to submit it through BIPS and receive it by a Python application using the [https://docs.python.org/3/c-api/buffer.html Buffer Protocol]. Python can handle these buffers in an agnostic fashion or cast them to NumPy straight-forward without any memory copy. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | [[File:bips-usecase1.png|500px|frameless|center|BIPS communication between one Producer and N Consumers]] | |
| − | |||
| − | + | * '''Buffer exchange between applications in containers''' | |
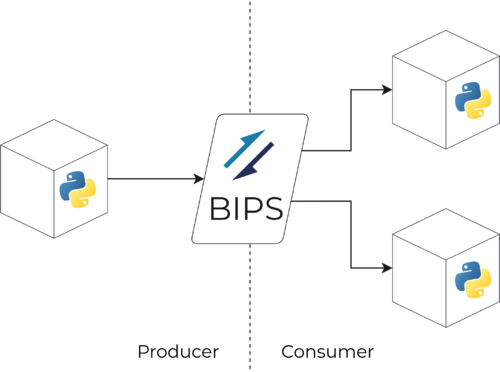
| − | + | BIPS allows zero-copy communication between applications isolated through containers. This makes BIPS a friend in your applications based on '''microservices''' without requiring any other container or process for the data exchange. | |
| − | + | [[File:bips-usecase2.png|500px|frameless|center|BIPS communication between one Producer and N Consumers in containers]] | |
| − | '' | + | ''TensorFlow, the TensorFlow logo, and any related marks are trademarks of Google Inc. PyTorch, the PyTorch logo and any related marks are trademarks of The Linux Foundation. SciPy is developed in the open on GitHub, through the consensus of the SciPy and wider scientific Python community. The Python logo is a trademark of the Python Software Foundation'' |
| − | |||
| − | + | For testing purposes, RidgeRun offers an evaluation version. Please refer to [[BIPS/Contact_Us| Contact Us]]. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | == Supported Backends == | |
| − | + | BIPS is used to communicate processes that need to share information, which helps optimize memory usage and application performance. BIPS supports: | |
| + | |||
| + | * Shared Memory | ||
| + | * NVIDIA NvSciIPC (under development) | ||
| + | |||
| + | The backend is responsible for allocating the pool of buffers with a fixed size, which will be known before processing. This is to avoid expensive allocation and free operations at runtime and to avoid memory fragmentation. '''Shared Memory''' is a standard way to communicate data between processes (IPC - Inter Process Communication, see the diagram below). In this methodology, data is allocated in a commonplace. So, when any process updates some value in the shared zone, the other processes can see the updated value immediately. BIPS shared memory implementation is based on the POSIX Shared Memory [https://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man7/shm_overview.7.html (shm)] to offer great compatibility. | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 67: | Line 82: | ||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
| − | === | + | == Tested Platforms == |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Since BIPS is based on POSIX, it is compatible with POSIX-complaint systems. We have tested it on: | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | * x86-64 (Linux) | |
| + | ** Intel-based systems | ||
| + | ** AMD-based systems | ||
| + | * ARM 64-bit (Linux) | ||
| + | ** NVIDIA Jetson Nano | ||
| + | ** NVIDIA Jetson Xavier | ||
| + | ** NVIDIA Jetson Orin | ||
| + | ** NVIDIA Jetson TX2 | ||
| − | < | + | <center> |
| − | [[ | + | <table> |
| − | < | + | <tr> |
| + | <td> | ||
| + | <html> | ||
| + | <div id='product-component-1674687854242'></div> | ||
| + | <script type="text/javascript"> | ||
| + | /*<![CDATA[*/ | ||
| + | (function () { | ||
| + | var scriptURL = 'https://sdks.shopifycdn.com/buy-button/latest/buy-button-storefront.min.js'; | ||
| + | if (window.ShopifyBuy) { | ||
| + | if (window.ShopifyBuy.UI) { | ||
| + | ShopifyBuyInit(); | ||
| + | } else { | ||
| + | loadScript(); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } else { | ||
| + | loadScript(); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | function loadScript() { | ||
| + | var script = document.createElement('script'); | ||
| + | script.async = true; | ||
| + | script.src = scriptURL; | ||
| + | (document.getElementsByTagName('head')[0] || document.getElementsByTagName('body')[0]).appendChild(script); | ||
| + | script.onload = ShopifyBuyInit; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | function ShopifyBuyInit() { | ||
| + | var client = ShopifyBuy.buildClient({ | ||
| + | domain: 'ridgerun1.myshopify.com', | ||
| + | storefrontAccessToken: 'b0ca98633a82de5d2f63cd51f5af30ac', | ||
| + | }); | ||
| + | ShopifyBuy.UI.onReady(client).then(function (ui) { | ||
| + | ui.createComponent('product', { | ||
| + | id: '7777398620347', | ||
| + | node: document.getElementById('product-component-1674687854242'), | ||
| + | moneyFormat: '%24%7B%7Bamount%7D%7D', | ||
| + | options: { | ||
| + | "product": { | ||
| + | "styles": { | ||
| + | "product": { | ||
| + | "@media (min-width: 601px)": { | ||
| + | "max-width": "calc(25% - 20px)", | ||
| + | "margin-left": "20px", | ||
| + | "margin-bottom": "50px" | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | "button": { | ||
| + | "font-family": "Open Sans, sans-serif", | ||
| + | "font-weight": "bold", | ||
| + | "font-size": "18px", | ||
| + | "padding-top": "17px", | ||
| + | "padding-bottom": "17px", | ||
| + | ":hover": { | ||
| + | "background-color": "#0187a7" | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | "background-color": "#0196ba", | ||
| + | ":focus": { | ||
| + | "background-color": "#0187a7" | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | "border-radius": "5px", | ||
| + | "padding-left": "50px", | ||
| + | "padding-right": "50px" | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | "quantityInput": { | ||
| + | "font-size": "18px", | ||
| + | "padding-top": "17px", | ||
| + | "padding-bottom": "17px" | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | "text": { | ||
| + | "button": "Add to cart" | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | "googleFonts": [ | ||
| + | "Open Sans" | ||
| + | ] | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | "productSet": { | ||
| + | "styles": { | ||
| + | "products": { | ||
| + | "@media (min-width: 601px)": { | ||
| + | "margin-left": "-20px" | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | "modalProduct": { | ||
| + | "contents": { | ||
| + | "img": false, | ||
| + | "imgWithCarousel": true, | ||
| + | "button": false, | ||
| + | "buttonWithQuantity": true | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | "styles": { | ||
| + | "product": { | ||
| + | "@media (min-width: 601px)": { | ||
| + | "max-width": "100%", | ||
| + | "margin-left": "0px", | ||
| + | "margin-bottom": "0px" | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | "button": { | ||
| + | "font-family": "Open Sans, sans-serif", | ||
| + | "font-weight": "bold", | ||
| + | "font-size": "18px", | ||
| + | "padding-top": "17px", | ||
| + | "padding-bottom": "17px", | ||
| + | ":hover": { | ||
| + | "background-color": "#0187a7" | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | "background-color": "#0196ba", | ||
| + | ":focus": { | ||
| + | "background-color": "#0187a7" | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | "border-radius": "5px", | ||
| + | "padding-left": "50px", | ||
| + | "padding-right": "50px" | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | "quantityInput": { | ||
| + | "font-size": "18px", | ||
| + | "padding-top": "17px", | ||
| + | "padding-bottom": "17px" | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | "googleFonts": [ | ||
| + | "Open Sans" | ||
| + | ] | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | "option": {}, | ||
| + | "cart": { | ||
| + | "styles": { | ||
| + | "button": { | ||
| + | "font-family": "Open Sans, sans-serif", | ||
| + | "font-weight": "bold", | ||
| + | "font-size": "18px", | ||
| + | "padding-top": "17px", | ||
| + | "padding-bottom": "17px", | ||
| + | ":hover": { | ||
| + | "background-color": "#0187a7" | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | "background-color": "#0196ba", | ||
| + | ":focus": { | ||
| + | "background-color": "#0187a7" | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | "border-radius": "5px" | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | "title": { | ||
| + | "color": "#4c4c4c" | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | "header": { | ||
| + | "color": "#4c4c4c" | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | "lineItems": { | ||
| + | "color": "#4c4c4c" | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | "subtotalText": { | ||
| + | "color": "#4c4c4c" | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | "subtotal": { | ||
| + | "color": "#4c4c4c" | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | "notice": { | ||
| + | "color": "#4c4c4c" | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | "currency": { | ||
| + | "color": "#4c4c4c" | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | "close": { | ||
| + | "color": "#4c4c4c", | ||
| + | ":hover": { | ||
| + | "color": "#4c4c4c" | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | "empty": { | ||
| + | "color": "#4c4c4c" | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | "noteDescription": { | ||
| + | "color": "#4c4c4c" | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | "discountText": { | ||
| + | "color": "#4c4c4c" | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | "discountIcon": { | ||
| + | "fill": "#4c4c4c" | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | "discountAmount": { | ||
| + | "color": "#4c4c4c" | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | "googleFonts": [ | ||
| + | "Open Sans" | ||
| + | ] | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | "toggle": { | ||
| + | "styles": { | ||
| + | "toggle": { | ||
| + | "font-family": "Open Sans, sans-serif", | ||
| + | "font-weight": "bold", | ||
| + | "background-color": "#0196ba", | ||
| + | ":hover": { | ||
| + | "background-color": "#0187a7" | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | ":focus": { | ||
| + | "background-color": "#0187a7" | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | "count": { | ||
| + | "font-size": "18px" | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | "googleFonts": [ | ||
| + | "Open Sans" | ||
| + | ] | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | "lineItem": { | ||
| + | "styles": { | ||
| + | "variantTitle": { | ||
| + | "color": "#4c4c4c" | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | "title": { | ||
| + | "color": "#4c4c4c" | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | "price": { | ||
| + | "color": "#4c4c4c" | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | "fullPrice": { | ||
| + | "color": "#4c4c4c" | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | "discount": { | ||
| + | "color": "#4c4c4c" | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | "discountIcon": { | ||
| + | "fill": "#4c4c4c" | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | "quantity": { | ||
| + | "color": "#4c4c4c" | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | "quantityIncrement": { | ||
| + | "color": "#4c4c4c", | ||
| + | "border-color": "#4c4c4c" | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | "quantityDecrement": { | ||
| + | "color": "#4c4c4c", | ||
| + | "border-color": "#4c4c4c" | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | "quantityInput": { | ||
| + | "color": "#4c4c4c", | ||
| + | "border-color": "#4c4c4c" | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | }); | ||
| + | }); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | })(); | ||
| + | /*]]>*/ | ||
| + | </script> | ||
| + | </html> | ||
| + | <td> | ||
| + | {{spaces|75}}<div align="right">{{ContactUs Button}}</div> | ||
| + | <td> | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | </tr></table> | ||
| + | </center> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
|- | |- | ||
Latest revision as of 10:59, 26 January 2023
|
Buffer Interprocess Sharing! Buffer Interprocess Sharing.
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Buffer Interprocess Sharing | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
This wiki is a user guide for our Buffer Interprocess Sharing project. ContentsWhat is Buffer Interprocess Sharing?Buffer Interprocess Sharing, or BIPS, is RidgeRun's optimized IPC library fully compatible with C++ and Python. In this case, BIPS allows sharing of data buffers between two or more processes with zero copy. They can be classified as Producers or Consumers according to their role in the system. The producer is responsible for generating and filling in the information on the buffers that the Consumers will read. The synchronization between these entities is handled by the Signaler, which ensures that all operations are concurrent-safe. This means that Consumers can only read buffers that are fully written by Producers and that Producers can only write buffers already read by Producers. These buffers are created and managed by a shared structure known as the Buffer Pool, which has a fixed capacity. The Signaler handles the synchronization between the BP and the Consumers/Producers. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Use casesWondering how and when to use BIPS? BIPS is a solution to exchange memory buffers between two isolated processes with zero copies without requiring additional processes. You can find BIPS in the following use cases:
BIPS allows communication between C++ and Python back and forth. A particular case is using a GStreamer capture application that requires transmitting the frames captured by a camera to a PyTorch-based Python application. From C++, you can define an agnostic memory buffer to submit it through BIPS and receive it by a Python application using the Buffer Protocol. Python can handle these buffers in an agnostic fashion or cast them to NumPy straight-forward without any memory copy.
BIPS allows zero-copy communication between applications isolated through containers. This makes BIPS a friend in your applications based on microservices without requiring any other container or process for the data exchange. TensorFlow, the TensorFlow logo, and any related marks are trademarks of Google Inc. PyTorch, the PyTorch logo and any related marks are trademarks of The Linux Foundation. SciPy is developed in the open on GitHub, through the consensus of the SciPy and wider scientific Python community. The Python logo is a trademark of the Python Software Foundation For testing purposes, RidgeRun offers an evaluation version. Please refer to Contact Us. Supported BackendsBIPS is used to communicate processes that need to share information, which helps optimize memory usage and application performance. BIPS supports:
The backend is responsible for allocating the pool of buffers with a fixed size, which will be known before processing. This is to avoid expensive allocation and free operations at runtime and to avoid memory fragmentation. Shared Memory is a standard way to communicate data between processes (IPC - Inter Process Communication, see the diagram below). In this methodology, data is allocated in a commonplace. So, when any process updates some value in the shared zone, the other processes can see the updated value immediately. BIPS shared memory implementation is based on the POSIX Shared Memory (shm) to offer great compatibility.
Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
Tested PlatformsSince BIPS is based on POSIX, it is compatible with POSIX-complaint systems. We have tested it on:
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
RidgeRun Support | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
RidgeRun provides support for embedded Linux development for NVIDIA, Xilinx, Freescale/NXP, and Texas Instruments platforms, specializing in multimedia applications. This page contains detailed guides and information on how to get started with Buffer Interprocess Sharing and start using its full capabilities. To get up-to-speed with your Buffer Interprocess Sharing, start by clicking below:
Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||