Difference between revisions of "GstWebRTC - Custom Signaling"
m |
|||
| (13 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | {{GstWebRTC/Head|previous=Predefined Signaling|next=API Reference|metakeywords=Gstreamer WebRTC Basics,Plugin Overview,Gstreamer WebRTC Plugin Overview,WebRTC Basics,Signaler,signaler-obj,WebRTC Signaler,Custom Signaler,signaling}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | This page provides the basics on how to implement custom signalers. In particular, this page describes how to integrate the custom signaler with the project's build system. The [[GstWebRTC - API Reference | API Reference]] shows how to develop a custom signaler that interacts with | + | This page provides the basics on how to implement custom signalers. In particular, this page describes how to integrate the custom signaler with the project's build system. The [[GstWebRTC - API Reference | API Reference]] shows how to develop a custom signaler that interacts with GstRrWebRTC state machine. |
==Custom Signaling Basics== | ==Custom Signaling Basics== | ||
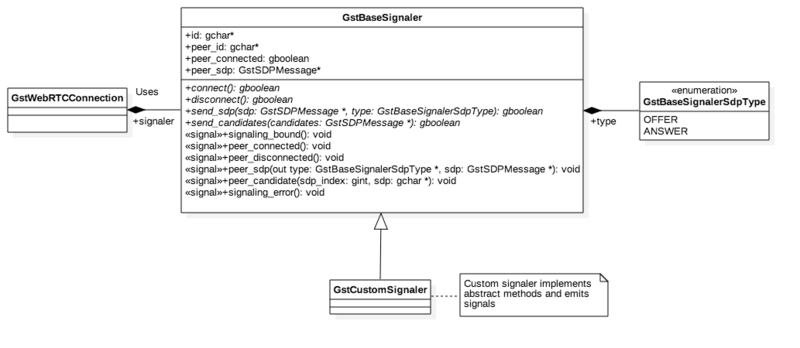
| − | Custom signalers are implemented by subclassing the GstBaseSignaler class. By doing so, the new signaler is integrated into | + | Custom signalers are implemented by subclassing the GstBaseSignaler class. By doing so, the new signaler is integrated into GstRrWebRTC state machine logic. The diagram in Figure 1 summarizes the concept: |
| − | [[File:gstwebrtc-uml-signaler.png|Figure 1. UML Diagram of Concrete Signalers]] | + | [[File:gstwebrtc-uml-signaler.png|800px|center|Figure 1. UML Diagram of Concrete Signalers]] |
| + | ==Integrating a Custom Signaling== | ||
| + | There are two ways a custom signaler can be integrated into the project. The first one is to build the new signaler along with the GstRrWebRTC project. In this case the signaler will be part of the project's binaries and the signaler's properties will be shown in the inspect output. The second way to integrate an external signaler is by doing it at runtime via the '''signaler-obj'''. In this case the signaler is built in an independent project and passed to the WebRTC state machine at runtime. The following subsections present further details. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | ===Integrating Into GstRrWebRTC Project=== | ||
| − | + | The easiest way to integrate a custom signaler is to extend the project's build system to construct the new code. The following points summarize the steps necessary to integrate a custom signaler named '''GstExampleSignaler'''. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | The easiest way to integrate a custom signaler is to extend the project's build system to construct the new code. The following points summarize the steps necessary to integrate | ||
1. Specify the new sources: | 1. Specify the new sources: | ||
| Line 28: | Line 24: | ||
At the end of ''gst/webrtc/Makefile.am'': | At the end of ''gst/webrtc/Makefile.am'': | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang=bash lines=1> | <syntaxhighlight lang=bash lines=1> | ||
| − | + | libgstrrwebrtc_la_SOURCES += gstexamplesignaler.c | |
noinst_HEADERS += gstexamplesignaler.h | noinst_HEADERS += gstexamplesignaler.h | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
2. Specify extra compile and link flags (if needed): | 2. Specify extra compile and link flags (if needed): | ||
| Line 36: | Line 33: | ||
At the end of ''gst/webrtc/Makefile.am'': | At the end of ''gst/webrtc/Makefile.am'': | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang=bash lines=1> | <syntaxhighlight lang=bash lines=1> | ||
| − | + | libgstrrwebrtc_la_CFLAGS += -I/usr/include/dependency | |
| − | + | libgstrrwebrtc_la_LIBADD += -L/usr/lib/dependency -ldependency | |
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
Alternatively, for advanced users, if the dependencies export a pkg-config file, the '''PKG_CHECK_MODULES''' may be used in the '''configure.ac''' and use the generated flags in this makefile. | Alternatively, for advanced users, if the dependencies export a pkg-config file, the '''PKG_CHECK_MODULES''' may be used in the '''configure.ac''' and use the generated flags in this makefile. | ||
| + | |||
3. Regenerate Makefiles: | 3. Regenerate Makefiles: | ||
| Line 50: | Line 48: | ||
sudo make install | sudo make install | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
===Integrating From ExternalProject=== | ===Integrating From ExternalProject=== | ||
| − | An alternative way to integrate an external signaler is to do it at runtime via the '''signaler-obj''' property. This is specially useful for signalers whose licensing is different and more restrictive than the one shipped with | + | An alternative way to integrate an external signaler is to do it at runtime via the '''signaler-obj''' property. This is specially useful for signalers whose licensing is different and more restrictive than the one shipped with GstRrWebRTC. As such, the signaler can be distributed independently. |
If both the '''signaler-obj''' and the built-in '''signaler''' properties are set, the last property set will be the one finally configured. | If both the '''signaler-obj''' and the built-in '''signaler''' properties are set, the last property set will be the one finally configured. | ||
| − | Programmatically, an application would set the new signaler in the | + | Programmatically, an application would set the new signaler in the GstRrWebRTC element similar to the following: |
<syntaxhighlight lang=c lines=1> | <syntaxhighlight lang=c lines=1> | ||
GstElement * webrtcbin; | GstElement * webrtcbin; | ||
| Line 67: | Line 66: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | }} | + | {{GstWebRTC/Foot|previous=Predefined Signaling|next=API Reference}} |
Latest revision as of 10:13, 9 March 2023
| GstWebRTC | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||||||
| WebRTC Fundamentals | ||||||||
| GstWebRTC Basics | ||||||||
|
||||||||
| Evaluating GstWebRTC | ||||||||
| Getting the code | ||||||||
| Building GstWebRTC | ||||||||
| Examples | ||||||||
|
||||||||
| MCU Demo Application | ||||||||
| Contact Us |
This page provides the basics on how to implement custom signalers. In particular, this page describes how to integrate the custom signaler with the project's build system. The API Reference shows how to develop a custom signaler that interacts with GstRrWebRTC state machine.
Contents
Custom Signaling Basics
Custom signalers are implemented by subclassing the GstBaseSignaler class. By doing so, the new signaler is integrated into GstRrWebRTC state machine logic. The diagram in Figure 1 summarizes the concept:
Integrating a Custom Signaling
There are two ways a custom signaler can be integrated into the project. The first one is to build the new signaler along with the GstRrWebRTC project. In this case the signaler will be part of the project's binaries and the signaler's properties will be shown in the inspect output. The second way to integrate an external signaler is by doing it at runtime via the signaler-obj. In this case the signaler is built in an independent project and passed to the WebRTC state machine at runtime. The following subsections present further details.
Integrating Into GstRrWebRTC Project
The easiest way to integrate a custom signaler is to extend the project's build system to construct the new code. The following points summarize the steps necessary to integrate a custom signaler named GstExampleSignaler.
1. Specify the new sources:
At the end of gst/webrtc/Makefile.am:
libgstrrwebrtc_la_SOURCES += gstexamplesignaler.c
noinst_HEADERS += gstexamplesignaler.h
2. Specify extra compile and link flags (if needed):
At the end of gst/webrtc/Makefile.am:
libgstrrwebrtc_la_CFLAGS += -I/usr/include/dependency
libgstrrwebrtc_la_LIBADD += -L/usr/lib/dependency -ldependency
Alternatively, for advanced users, if the dependencies export a pkg-config file, the PKG_CHECK_MODULES may be used in the configure.ac and use the generated flags in this makefile.
3. Regenerate Makefiles:
At the root of the project:
./autogen.sh
make
sudo make install
Integrating From ExternalProject
An alternative way to integrate an external signaler is to do it at runtime via the signaler-obj property. This is specially useful for signalers whose licensing is different and more restrictive than the one shipped with GstRrWebRTC. As such, the signaler can be distributed independently.
If both the signaler-obj and the built-in signaler properties are set, the last property set will be the one finally configured.
Programmatically, an application would set the new signaler in the GstRrWebRTC element similar to the following:
GstElement * webrtcbin;
GstExampleSignaler *examplesignaler;
...
g_object_set (webrtcbin, "signaler-obj", GST_BASE_SIGNALER(example signaler), NULL);