Difference between revisions of "Birds Eye View/Getting the Code/Building and Installation Guide"
m (→Birds eye view library and examples installation) |
(→Building OpenCV with GStreamer support) |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<noinclude> | <noinclude> | ||
| − | {{Birds Eye View/Head|next=Getting_Started|previous=Getting the Code/ | + | {{Birds Eye View/Head|next=Getting_Started|previous=Getting the Code/Evaluation|keywords=|title=Birds Eye View Building and Installation Guide}} |
</noinclude> | </noinclude> | ||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
|type=notice | |type=notice | ||
|small=left | |small=left | ||
| − | |issue='''NOTE:''' The manual compilation of OpenCV is just needed if you want to use the library to load video from cameras, due the need to use GStreamer as the video opener and select the correct video formats for OpenCV. If you do not require this functionality, this compilation can be skipped. | + | |issue='''NOTE:''' The manual compilation of OpenCV is just needed if you want to use the library to load video from cameras, due to the need to use GStreamer as the video opener and select the correct video formats for OpenCV. If you do not require this functionality, this compilation can be skipped. |
|style=width: auto; margin-right: 0px; | |style=width: auto; margin-right: 0px; | ||
|textstyle=width: auto; | |textstyle=width: auto; | ||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
sudo apt-get install build-essential | sudo apt-get install build-essential | ||
sudo apt-get install cmake git libgtk2.0-dev pkg-config libavcodec-dev libavformat-dev libswscale-dev | sudo apt-get install cmake git libgtk2.0-dev pkg-config libavcodec-dev libavformat-dev libswscale-dev | ||
| − | sudo apt-get install python-dev python-numpy libtbb2 libtbb-dev libjpeg-dev libpng-dev libtiff-dev | + | sudo apt-get install python-dev python-numpy libtbb2 libtbb-dev libjpeg-dev libpng-dev libtiff-dev libwebp-dev libdc1394-22-dev |
pip3 install numpy | pip3 install numpy | ||
pip3 install imutils | pip3 install imutils | ||
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
git clone https://github.com/opencv/opencv.git | git clone https://github.com/opencv/opencv.git | ||
cd opencv/ | cd opencv/ | ||
| − | git checkout 4.1.0 | + | git checkout 4.1.0 |
| + | cd .. | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
| Line 63: | Line 64: | ||
git clone https://github.com/opencv/opencv_contrib.git | git clone https://github.com/opencv/opencv_contrib.git | ||
cd opencv_contrib/ | cd opencv_contrib/ | ||
| − | git checkout 4.1.0 | + | git checkout 4.1.0 |
| + | cd .. | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
| Line 69: | Line 71: | ||
|type=notice | |type=notice | ||
|small=left | |small=left | ||
| − | |issue='<span style="color:#FF0000"> *Disclaimer: </span>''' On newer relases of OpenCV, some algorithms are proprietary and not for commercial use. This is a research project, therefore be informed that you can't use the line '''-D OPENCV_ENABLE_NONFREE=ON''' for commercial purposes. | + | |issue='<span style="color:#FF0000"> *Disclaimer: </span>''' On newer relases of OpenCV, some algorithms are proprietary and not for commercial use. This is a research project and therefore here we add them even though they might not be used, therefore be informed that you can't use the line '''-D OPENCV_ENABLE_NONFREE=ON''' for commercial purposes. |
|style=width: auto; margin-right: 0px; | |style=width: auto; margin-right: 0px; | ||
|textstyle=width: auto; | |textstyle=width: auto; | ||
| Line 76: | Line 78: | ||
'''4. Configure with required flags''' | '''4. Configure with required flags''' | ||
<source lang="bash"> | <source lang="bash"> | ||
| + | cd opencv/ | ||
mkdir build | mkdir build | ||
cd build | cd build | ||
| Line 96: | Line 99: | ||
'''5. Check configuration log''' | '''5. Check configuration log''' | ||
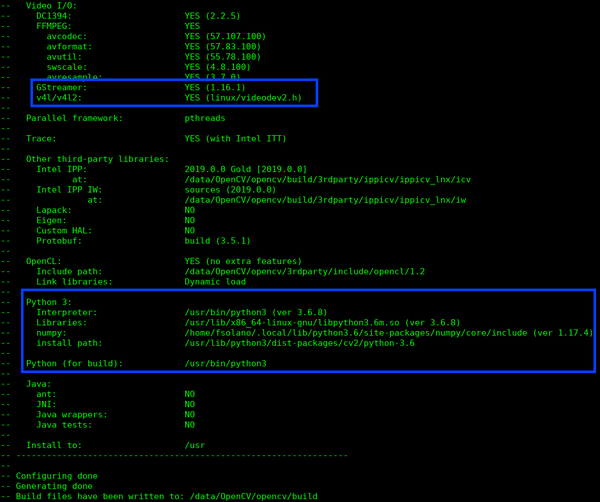
| − | ✔ Verify if it has Python 3: section and all interpreter and path are right. (If they aren’t there, check the | + | ✔ Verify if it has Python 3: section and all interpreter and path are right. (If they aren’t there, check the NumPy package) |
| − | ✔ Check the GStreamer section. (If it does not indicate '''YES''', go check GStreamer lib package) | + | ✔ Check the GStreamer section. (If it does not indicate '''YES''', go check the GStreamer lib package) |
[[File:Opencv configure.png|600px|center]] | [[File:Opencv configure.png|600px|center]] | ||
| Line 122: | Line 125: | ||
* [https://developer.ridgerun.com/wiki/index.php?title=Install_OpenCV_with_CUDA_support_on_Jetson_Boards Install OpenCV with CUDA support on Jetson boards] | * [https://developer.ridgerun.com/wiki/index.php?title=Install_OpenCV_with_CUDA_support_on_Jetson_Boards Install OpenCV with CUDA support on Jetson boards] | ||
| − | in order to properly configure, compile and install OpenCV, in a native way; it is worth | + | in order to properly configure, compile, and install OpenCV, in a native way; it is worth mentioning that this is not a cross-compilation. |
== Build library and examples == | == Build library and examples == | ||
| Line 169: | Line 172: | ||
==== Meson version ==== | ==== Meson version ==== | ||
| − | On Ubuntu 18.04.1 LTS, the Meson install usually has a 0.45.1 version, however the project requires at least 0.50. A newer version of Meson can be installed using Pip in the following way: | + | On Ubuntu 18.04.1 LTS, the Meson install usually has a 0.45.1 version, however, the project requires at least 0.50. A newer version of Meson can be installed using Pip in the following way: |
<syntaxhighlight lang='bash'> | <syntaxhighlight lang='bash'> | ||
| Line 175: | Line 178: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | This usually installs the latest version of Meson available for your system. However, this is just accessible from the Python environment. In order to make it system wide do: | + | This usually installs the latest version of Meson available for your system. However, this is just accessible from the Python environment. In order to make it system-wide do: |
<syntaxhighlight lang='bash'> | <syntaxhighlight lang='bash'> | ||
| Line 200: | Line 203: | ||
== Patch to support 4 USB cameras == | == Patch to support 4 USB cameras == | ||
| − | When using more than 2 USB cameras it may be necessary to jump over the bandwidth restriction imposed by the generic | + | When using more than 2 USB cameras it may be necessary to jump over the bandwidth restriction imposed by the generic USB driver, which is not capable of requesting the correct image size, therefore, requests the max size. It is necessary to recompile the driver after applying the required patch. |
<br> | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 230: | Line 233: | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
| + | If you have problems trying to download the kernel sources via APT, you can download them as follows: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Find the release of L4T you are currently working with: | ||
| + | <source lang="bash"> | ||
| + | head -n 1 /etc/nv_tegra_release | ||
| + | dpkg -l | grep ‘nvidia-l4t-core | ||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Go to the [https://developer.nvidia.com/embedded/linux-tegra-archive Linux Tegra Archive] page and click on the L4T version button according to the output you've got in the previous step. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Go to the '''Driver Details''' chart and click on '''L4T Driver Package (BSP) Sources''' to download the whole driver package. It will start the '''public_sources.tbz2''' package downloading. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * You will find a file named as '''kernel_src.tbz2''' inside the '''public_sources.tbz2''' package located in the <code>/Linux_for_Tegra/source/public/</code> folder. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Extract the '''kernel_src.tbz2''' from the '''public_sources.tbz2''' package and then, extract the content of the '''kernel_src.tbz2''' tarball. | ||
| + | * You should have access to the UVC sources: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <source lang="bash"> | ||
| + | cd kernel/kernel-4.9/drivers/media/usb/uvc/ | ||
| + | mkdir patches | ||
| + | cd patches | ||
| + | </source> | ||
'''2. Create the patch file''' | '''2. Create the patch file''' | ||
| Line 255: | Line 280: | ||
static int uvc_get_video_ctrl(struct uvc_streaming *stream, | static int uvc_get_video_ctrl(struct uvc_streaming *stream, | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | {{Ambox | ||
| + | |type=notice | ||
| + | |small=left | ||
| + | |issue='''<span style="color:#FF0000"> *NOTE: </span>''' The UVC sources may change with each version of the kernel sources. So, you probably will need to add the green lines manually instead of applying the patch with <code>quilt</code>. | ||
| + | |style=width: auto; margin-right: 0px; | ||
| + | |textstyle=width: auto; | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | <br> | ||
'''3. Setup the series file:''' | '''3. Setup the series file:''' | ||
| Line 279: | Line 314: | ||
<noinclude> | <noinclude> | ||
| − | {{Birds Eye View/Foot|Getting the Code/ | + | {{Birds Eye View/Foot|Getting the Code/Evaluation|Getting_Started}} |
</noinclude> | </noinclude> | ||
Latest revision as of 09:51, 22 October 2021
| Birds Eye View |
|---|
 |
| Introduction |
| Getting the Code |
| Getting Started |
| Examples |
| Library Docs |
| Performance |
| Contact Us |
Contents
Birds eye view library and examples installation
System Dependencies
Birds eye view has the following system dependencies:
- meson >= 0.50
- ninja
- boost
- opencv 3.1.0 (or higher version)
Meson, Ninja and Boost can be installed using the next command line (tested on Ubuntu 18.04.3):
sudo apt install meson ninja-build libboost-dev libjson-glib-dev
Building OpenCV with GStreamer support
NOTE: The manual compilation of OpenCV is just needed if you want to use the library to load video from cameras, due to the need to use GStreamer as the video opener and select the correct video formats for OpenCV. If you do not require this functionality, this compilation can be skipped. |
1. Install previous GStreamer dependencies
sudo apt-get install gstreamer1.0*
sudo apt install ubuntu-restricted-extras
sudo apt install libgstreamer1.0-dev libgstreamer-plugins-base1.0-dev
2. Install compiler and building dependencies
sudo apt-get install build-essential
sudo apt-get install cmake git libgtk2.0-dev pkg-config libavcodec-dev libavformat-dev libswscale-dev
sudo apt-get install python-dev python-numpy libtbb2 libtbb-dev libjpeg-dev libpng-dev libtiff-dev libwebp-dev libdc1394-22-dev
pip3 install numpy
pip3 install imutils
3. Obtain source code from Github
git clone https://github.com/opencv/opencv.git
cd opencv/
git checkout 4.1.0
cd ..
git clone https://github.com/opencv/opencv_contrib.git
cd opencv_contrib/
git checkout 4.1.0
cd ..
' *Disclaimer: On newer relases of OpenCV, some algorithms are proprietary and not for commercial use. This is a research project and therefore here we add them even though they might not be used, therefore be informed that you can't use the line -D OPENCV_ENABLE_NONFREE=ON for commercial purposes. |
4. Configure with required flags
cd opencv/
mkdir build
cd build
cmake -D CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=RELEASE \
-D CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/usr/local \
-D INSTALL_PYTHON_EXAMPLES=ON \
-D INSTALL_C_EXAMPLES=OFF \
-D PYTHON_EXECUTABLE=$(which python3) \
-D BUILD_opencv_python2=OFF \
-D PYTHON3_EXECUTABLE=$(which python3) \
-D PYTHON3_INCLUDE_DIR=$(python3 -c "from distutils.sysconfig import get_python_inc; print(get_python_inc())") \
-D PYTHON3_PACKAGES_PATH=$(python3 -c "from distutils.sysconfig import get_python_lib; print(get_python_lib())") \
-D WITH_GSTREAMER=ON \
-D OPENCV_EXTRA_MODULES_PATH=../../opencv_contrib/modules/ \
-D OPENCV_ENABLE_NONFREE=ON \
-D OPENCV_GENERATE_PKGCONFIG=YES \
-D BUILD_EXAMPLES=ON ..
5. Check configuration log
✔ Verify if it has Python 3: section and all interpreter and path are right. (If they aren’t there, check the NumPy package)
✔ Check the GStreamer section. (If it does not indicate YES, go check the GStreamer lib package)
6. Building
It will last some time. Please be patient.
sudo make -j4
7. Install the package
sudo make install
sudo ldconfig
Building OpenCV with GStreamer and CUDA support
If you are using a NVIDIA Jetson device, you can follow the instructions on the next wiki:
in order to properly configure, compile, and install OpenCV, in a native way; it is worth mentioning that this is not a cross-compilation.
Build library and examples
git clone https://gitlab.com/RidgeRun/rnd/bird-eye-view.git
cd bird-eye-view
mkdir build
cd build
meson ..
ninja
The library also supports several meson options to:
1. Build the library with OpenCV CUDA support. This boost library performance by using CUDA to compute heavy transformation methods on GPU.
meson -Dopencv-cuda=enabled ..
2. Build the library with profiling support. Please refer to Birds_Eye_View/Performance/Profiling to install dependencies
meson -Dprofiling=enabled ..
3. Build the library with documentation
meson -Ddoc=enabled ..
4. Build only the documentation
meson -Ddocs-only=enabled ..
Now you will find the example files:
- bevFromRectilinearImages
- bevFromFisheyeImages
- removeFisheyeFromImages
- bevFromRectilinearVideos
- bevFromCameras
Troubleshooting
Meson version
On Ubuntu 18.04.1 LTS, the Meson install usually has a 0.45.1 version, however, the project requires at least 0.50. A newer version of Meson can be installed using Pip in the following way:
sudo -H pip3 install meson
This usually installs the latest version of Meson available for your system. However, this is just accessible from the Python environment. In order to make it system-wide do:
sudo touch /usr/local/bin/meson
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/meson
and add the following on it:
#!/usr/bin/python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import re
import sys
from mesonbuild.mesonmain import main
if __name__ == '__main__':
sys.argv[0] = re.sub(r'(-script\.pyw?|\.exe)?$', '', sys.argv[0])
sys.exit(main())
With this, you can follow the steps to build without further issues.
Patch to support 4 USB cameras
When using more than 2 USB cameras it may be necessary to jump over the bandwidth restriction imposed by the generic USB driver, which is not capable of requesting the correct image size, therefore, requests the max size. It is necessary to recompile the driver after applying the required patch.
*Disclaimer: This patch is a 'hack' to trick the verification process when asking for resources to initialize the cameras. Needed to allow the use of 4 simultaneous usb cameras, however it was just used for testing purposes and may not be stable. |
1. Download the kernel source
sudo apt-get source linux-image-unsigned-$(uname -r)
cd $(uname -r)/drivers/media/usb/uvc/
mkdir patches
cd patches
If you get this error:
E: You must put some 'source' URIs in your sources.list
Run the following commands:
sudo cp /etc/apt/sources.list /etc/apt/sources.list~
sudo sed -Ei 's/^# deb-src /deb-src /' /etc/apt/sources.list
sudo apt-get update
If you have problems trying to download the kernel sources via APT, you can download them as follows:
- Find the release of L4T you are currently working with:
head -n 1 /etc/nv_tegra_release
dpkg -l | grep ‘nvidia-l4t-core
- Go to the Linux Tegra Archive page and click on the L4T version button according to the output you've got in the previous step.
- Go to the Driver Details chart and click on L4T Driver Package (BSP) Sources to download the whole driver package. It will start the public_sources.tbz2 package downloading.
- You will find a file named as kernel_src.tbz2 inside the public_sources.tbz2 package located in the
/Linux_for_Tegra/source/public/folder.
- Extract the kernel_src.tbz2 from the public_sources.tbz2 package and then, extract the content of the kernel_src.tbz2 tarball.
- You should have access to the UVC sources:
cd kernel/kernel-4.9/drivers/media/usb/uvc/
mkdir patches
cd patches
2. Create the patch file
vim 001-uvc-add-compressed-video-bandwidth-parameter.patch
Index: ./uvc_video.c
===================================================================
--- ./uvc_video.c
+++ ./uvc_video.c
@@ -161,6 +161,11 @@ static void uvc_fixup_video_ctrl(struct
ctrl->dwMaxPayloadTransferSize = bandwidth;
}
+
+ if (format->flags & UVC_FMT_FLAG_COMPRESSED) {
+ ctrl->dwMaxPayloadTransferSize = 0x300;
+ }
+
}
static int uvc_get_video_ctrl(struct uvc_streaming *stream,
*NOTE: The UVC sources may change with each version of the kernel sources. So, you probably will need to add the green lines manually instead of applying the patch with quilt. |
3. Setup the series file:
echo 001-uvc-add-compressed-video-bandwidth-parameter.patch > series
cd ..
4. Apply the patch:
quilt push
5. Compile and reload the kernel module:
sudo make -C /lib/modules/$(uname -r)/build M=$(pwd) modules
sudo rmmod uvcvideo
sudo insmod uvcvideo.ko